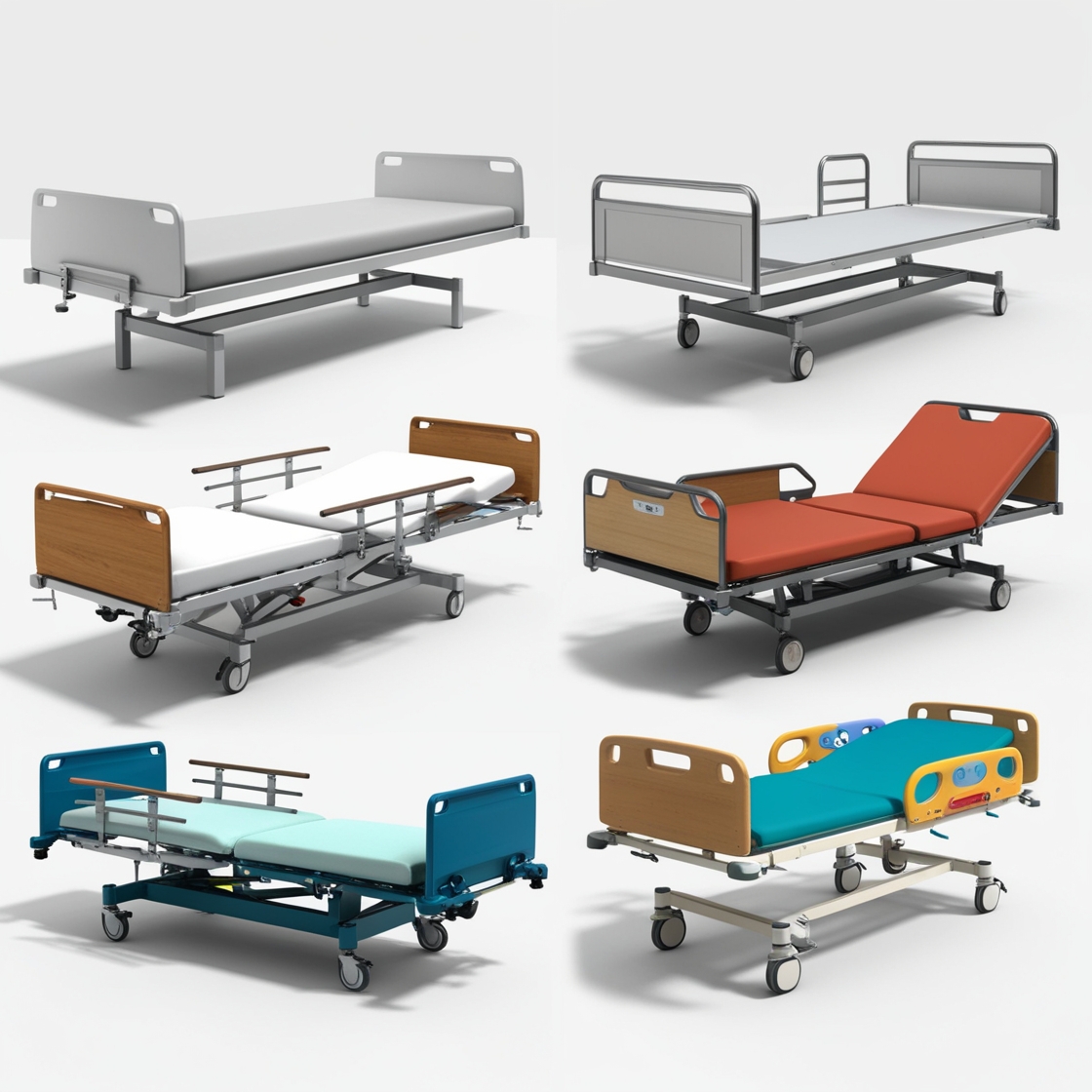
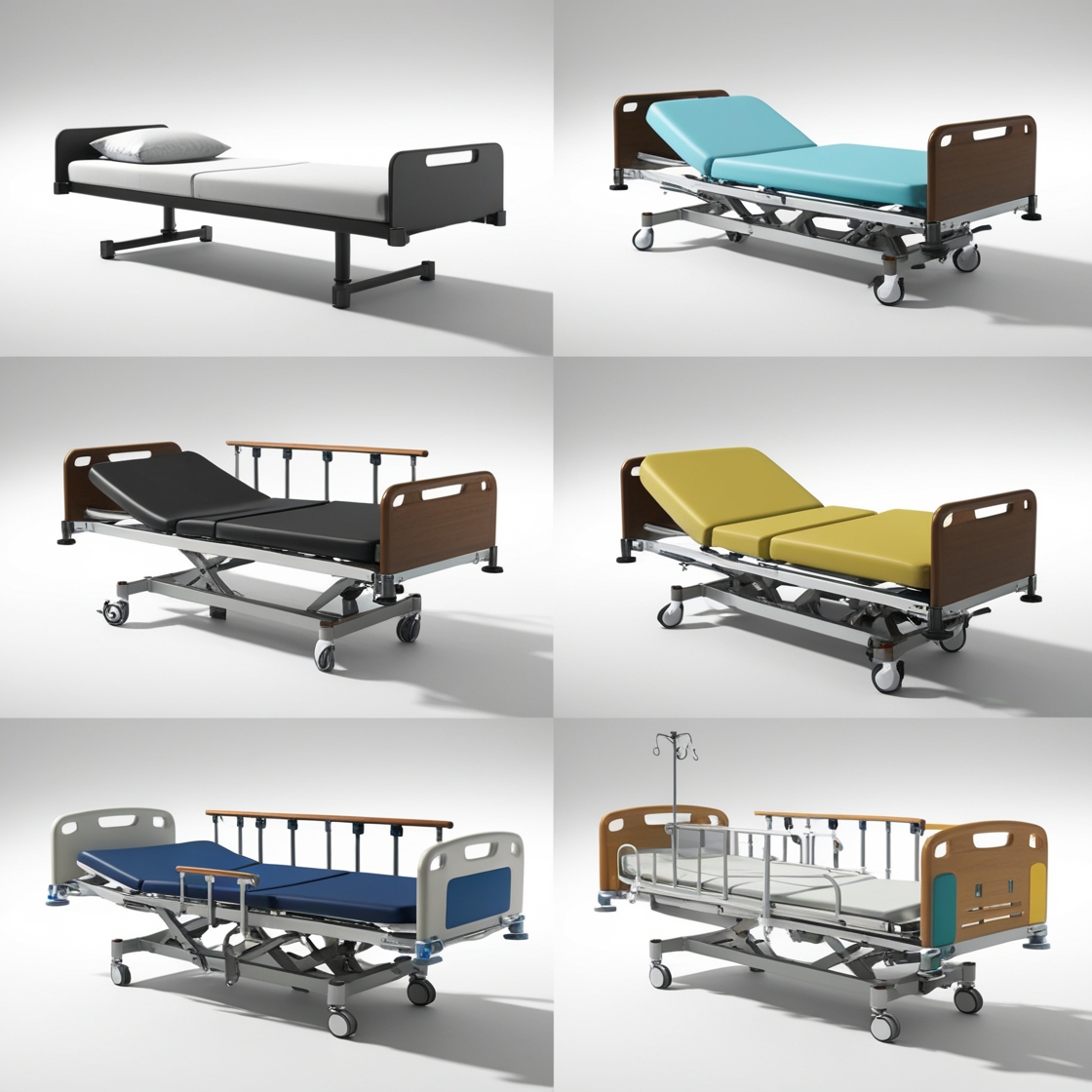
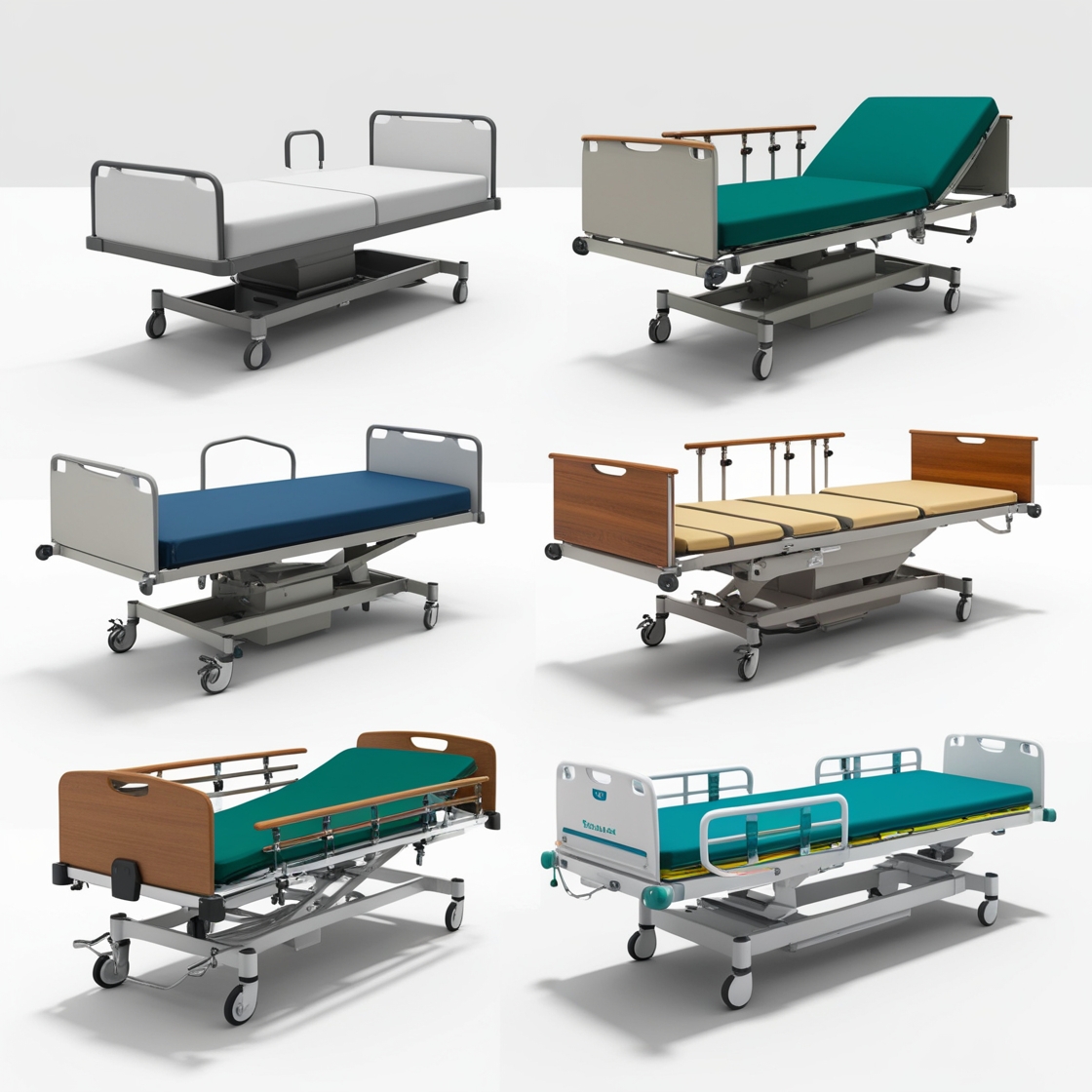
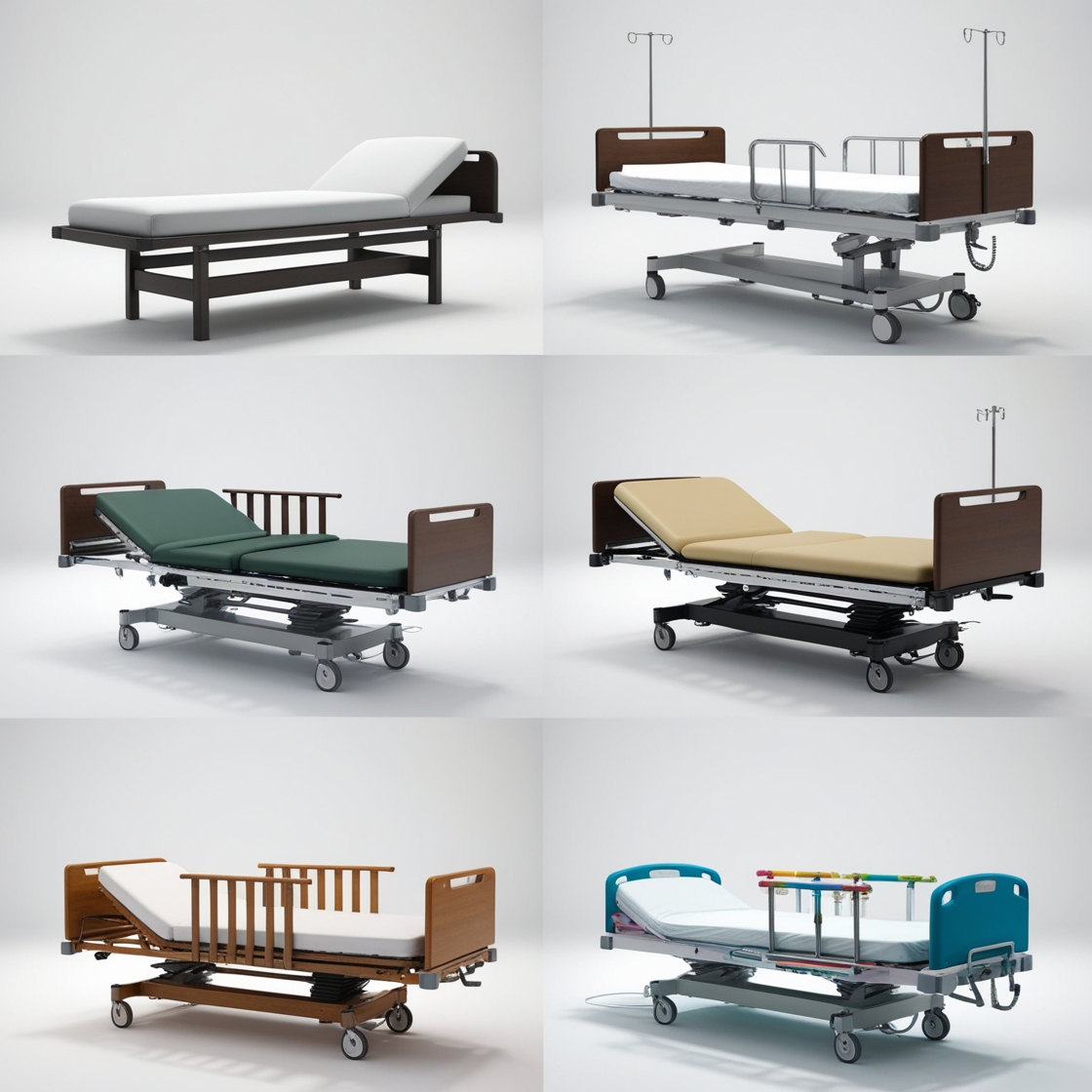
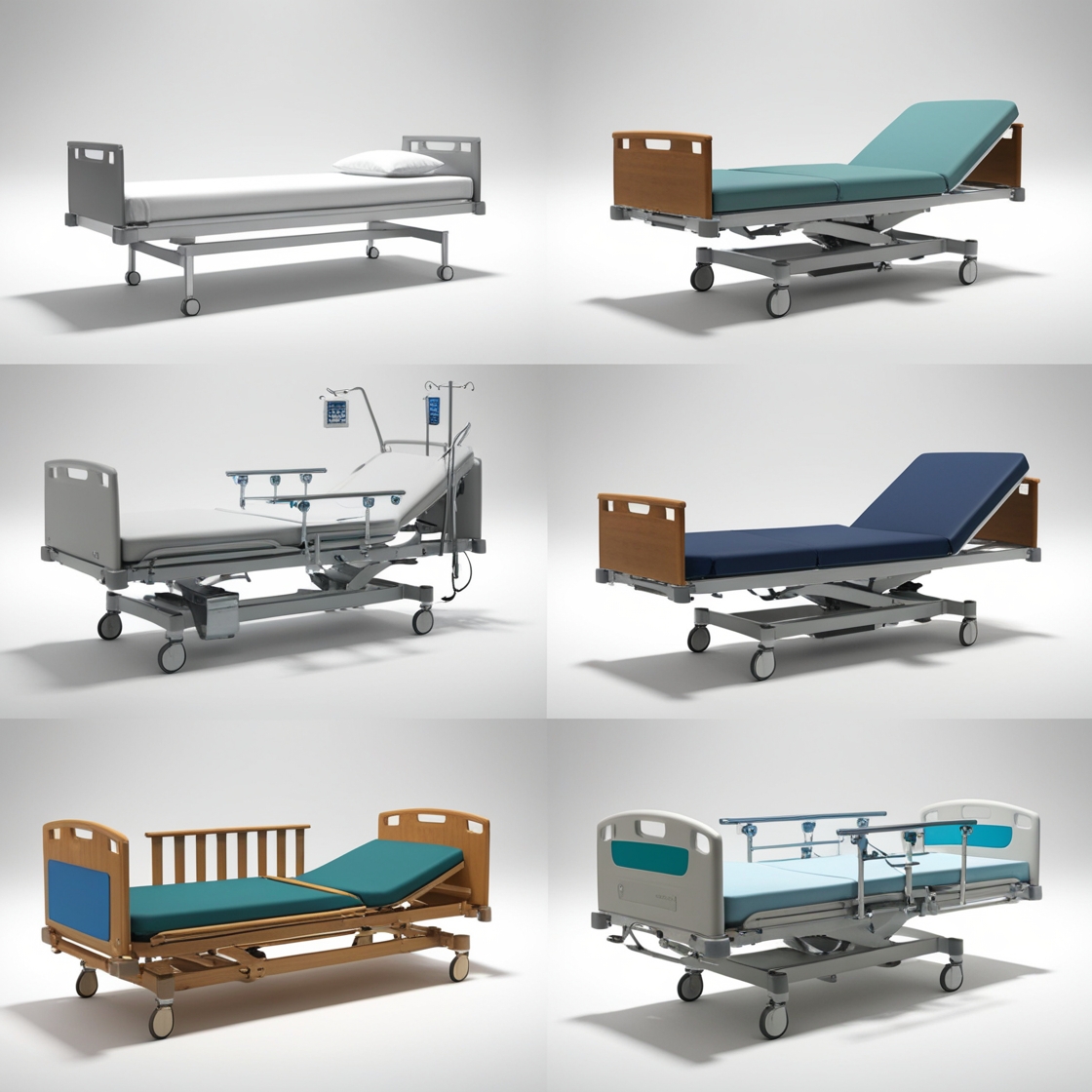
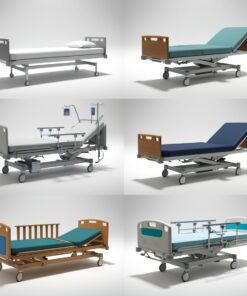
Hospital beds come in various types to cater to different medical needs and patient requirements. Here’s a list of the common types and their uses:
1. Manual Hospital Beds
- Description: Operated using a hand crank to adjust the bed’s height, head, and foot sections.
- Uses:
- Suitable for settings with limited electricity access.
- Ideal for patients who do not require frequent adjustments.
2. Semi-Electric Hospital Beds
- Description: Combine manual and electric functions. Typically, the head and foot adjustments are electric, while height adjustment is manual.
- Uses:
- Offers ease of adjustment for the patient or caregiver.
- Cost-effective compared to fully electric beds.
3. Fully Electric Hospital Beds
- Description: All adjustments (height, head, and foot sections) are controlled via an electric remote or panel.
- Uses:
- Provides maximum comfort for patients with mobility issues.
- Reduces caregiver effort.
- Common in hospitals, nursing homes, and home care.
4. Bariatric Beds
- Description: Specifically designed for obese patients, these beds are wider, stronger, and can support heavier weights.
- Uses:
- Ensures comfort and safety for overweight patients.
- Often equipped with reinforced frames and mattresses.
5. Adjustable Beds
- Description: Highly versatile beds with multiple positioning options.
- Uses:
- Suitable for patients requiring various therapeutic positions.
- Common in intensive care units (ICUs).
6. ICU Beds
- Description: Specialized beds equipped with advanced features like CPR positioning, cardiac chairs, and electronic controls.
- Uses:
- Designed for critically ill patients needing constant monitoring.
- Allow easy access for medical equipment and care.
7. Pediatric Beds
- Description: Smaller beds with safety rails, designed for children.
- Uses:
- Ensures safety for pediatric patients.
- Often used in pediatric wards and hospitals.
8. Low Beds
- Description: Beds that can be lowered close to the ground.
- Uses:
- Minimize the risk of injury from falls for elderly or restless patients.
- Suitable for patients who struggle to get in and out of bed.
9. Rotating Beds
- Description: Beds that rotate to help patients move or exit the bed with minimal effort.
- Uses:
- Beneficial for patients with mobility issues.
- Helps reduce pressure sores by changing body positions.
10. Stretchers or Transport Beds
- Description: Mobile beds designed for transporting patients.
- Uses:
- Used in emergency rooms, operating rooms, and patient transfers.
11. Air Mattress Beds (Alternating Pressure Beds)
- Description: Equipped with air bladders that alternate pressure to prevent bedsores.
- Uses:
- Ideal for immobile patients.
- Prevents and treats pressure ulcers.
12. Gatch Beds
- Description: Basic hospital beds with manual adjustments.
- Uses:
- Used in older hospitals or care settings with limited resources.
13. Recliner Beds
- Description: Beds that can transform into a chair position.
- Uses:
- Common in recovery rooms and for post-operative care.
- Suitable for patients who need a seated position for comfort or therapy.
14. Special Care Beds (e.g., Cardiac or Neurological Beds)
- Description: Designed for patients with specific medical conditions.
- Uses:
- Provide specific support for conditions like cardiac issues or neurological problems.
Each type of bed is tailored to meet unique patient care requirements, improving comfort, safety, and treatment outcomes.
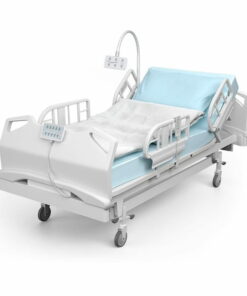
Adjustable Hospital beds:
Looking for comfor t and versatility in patient care? Our adjustable Hospital beds are designed to provide utmost comfor t and flexibility. With easy electronic controls, you can effor tlessly find the perfect position. Ensure your patient s’ well-being with our premium adjustable Hospital beds.
Related products
Hospital beds
R987.89 ex VAT
Hospital beds
R2,590.25 ex VAT
Hospital beds
R2,056.13 ex VAT
Hospital beds
R2,145.15 ex VAT
Hospital beds
R1,967.11 ex VAT
Hospital beds
R2,857.31 ex VAT
Hospital beds
R898.87 ex VAT
Hospital beds
R2,876.00 ex VAT