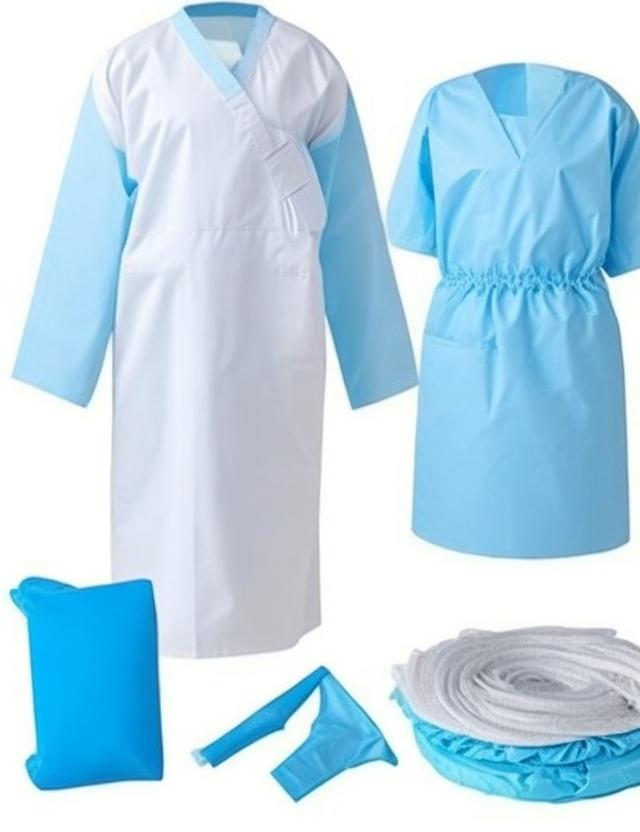
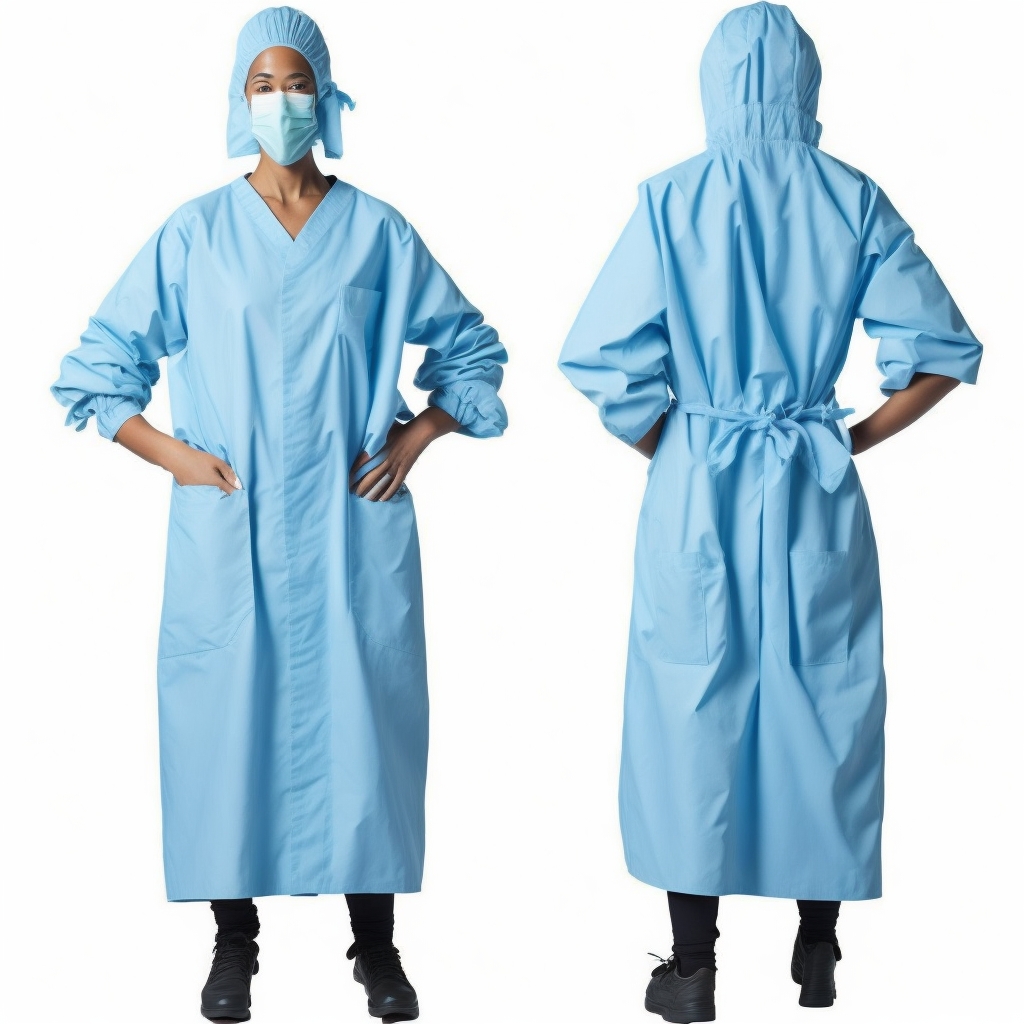
patient operation gown
R38.93 ex VAT
Hospital gowns are essential for maintaining hygiene, providing comfort, and ensuring patient safety in medical settings. Here’s a comprehensive list of types of hospital gowns and their uses:
Types of Hospital Gowns
- Standard Patient Gowns
- Description: Basic gowns typically made from cotton or a cotton-polyester blend, often with ties at the back or sides.
- Uses: Worn by patients undergoing routine examinations, tests, or procedures. Provides ease of access for medical staff and is designed for comfort during short-term use.
- Open-Back Gowns
- Description: Gowns with an open back, usually tied at the neck and waist.
- Uses: Commonly used in general medical settings to allow easy access for examinations and treatments while providing modesty.
- Isolation Gowns
- Description: Made from materials like polypropylene or polyethylene, designed to protect healthcare workers from exposure to bodily fluids and contaminants.
- Uses: Worn by healthcare professionals during procedures involving potential exposure to infectious materials or in isolation rooms to prevent the spread of infection.
- Surgical Gowns
- Description: High-level protective gowns made from sterile, fluid-resistant materials like non-woven fabric.
- Uses: Worn by surgeons and operating room staff to maintain a sterile field and prevent infection during surgeries and invasive procedures.
- Surgical Drapes
- Description: Larger, sterile sheets used to cover patients and surrounding areas during surgery.
- Uses: Maintain a sterile environment by covering the patient and the surgical area, protecting against contamination during operations.
- Procedure Gowns
- Description: Gowns made from lightweight, fluid-resistant materials, often used for specific diagnostic or minor procedures.
- Uses: Provide protection and hygiene during procedures such as endoscopies or minor surgeries.
- Delivery Gowns
- Description: Gowns designed specifically for labor and delivery, often made from soft, breathable materials.
- Uses: Worn by patients during childbirth to ensure comfort and ease of access for medical staff.
- Patient Transfer Gowns
- Description: Gowns with additional features like reinforced areas and ease of use for patient transfer.
- Uses: Facilitate the safe and efficient transfer of patients between different areas of a hospital, such as from a bed to a stretcher.
- Radiology Gowns
- Description: Gowns with lead shielding to protect against radiation exposure.
- Uses: Worn by patients during X-rays or other radiological procedures to minimize radiation exposure to areas not being examined.
- Bariatric Gowns
- Description: Gowns designed for larger patients, with extended sizes and additional room.
- Uses: Provide comfort and coverage for bariatric patients, ensuring a proper fit and ease of use.
Uses of Hospital Gowns
- Hygiene and Infection Control
- Function: Hospital gowns help maintain a clean environment and prevent the spread of infections by providing a barrier between the patient and medical staff.
- Comfort and Dignity
- Function: Designed to be comfortable and provide modesty for patients during medical examinations and procedures.
- Ease of Access
- Function: Allows healthcare professionals easy access to the patient’s body for medical procedures, examinations, or surgery while preserving patient privacy.
- Protection for Healthcare Workers
- Function: Isolation and surgical gowns protect healthcare workers from exposure to potentially infectious materials and bodily fluids.
- Sterility
- Function: Surgical gowns and drapes help maintain a sterile field during surgeries and invasive procedures, reducing the risk of infection.
- Radiation Protection
- Function: Radiology gowns with lead shielding protect patients from unnecessary radiation exposure during diagnostic imaging.
Each type of hospital gown is designed to meet specific needs within medical settings, ensuring safety, comfort, and hygiene for both patients and healthcare professionals.